Demo (python):
Robotic Arm Force Control Demo 1. Project introduction
This project, via the RealMan Python development package, completes the robotic arm connection, robotic arm version acquisition, API version acquisition, 6-DoF force control with movel for straight-line motion, force control application to move the trajectory downward, and termination of force control and disconnection.
2. Code structure
RMDemo_ForceControl/
│
├── README.md <- Core project document
├── requirements.txt <- List of project dependencies
├── setup.py <- Project installation script
│
├── src/ <- Project source code
│ ├── main.py <- Main procedure entry
│ └── core/ <- Core function or business logic code
│ └── demo_force_control.py <- Demo that completes the robotic arm connection, robotic arm version acquisition, API version acquisition, 6-DoF force control with movel for straight-line motion, force control application to move the trajectory downward, and termination of force control and disconnection.
└── Robotic_Arm/ <- RealMan robotic arm secondary development package3. Project download
Download RM_API2 locally via the link: development package download. Then, navigate to the RM_API2\Demo\RMDemo_Python directory, where you will find RMDemo_ForceControl.
4. Environment configuration
Required environment and dependencies for running in Windows and Linux environments:
| Item | Linux | Windows |
|---|---|---|
| System architecture | x86 architecture | - |
| python | 3.9 or higher | 3.9 or higher |
| Specific dependency | - | - |
Linux configuration
Refer to the python official website - linux to download and install python3.9.
After entering the project directory, open the terminal and run the following command to install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtWindows configuration
Refer to the python official website - Windows to download and install python3.9.
After entering the project directory, open the terminal and run the following command to install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt5. Notes
- This demo uses the RM65-S robotic arm as an example. Please modify the data in the code according to your actual situation.
- This demo requires the robotic arm to have 6-DoF force in order to be used.
6. User guide
6.1 Quick run
Follow these steps to quickly run the code:
Configuration of the IP address of the robotic arm : open the
demo_force_control.pyfile and modify the initialization parameters of theRobotArmControllerclass in themainfunction to the current IP address of the robotic arm. The default IP address is"192.168.1.18".python# Create a robot arm controller instance and connect to the robot arm robot_controller = RobotArmController("192.168.1.18", 8080, 3)Running via command line: navigate to the
RMDemo_ForceControldirectory in the terminal and enter the following command to run the Python script:bashpython ./src/main.pyRunning result: The execution results of the robotic arm will be displayed in the terminal.
(1) After running the script, the output result is as follows:
current api version: 0.2.9
Successfully connected to the robot arm: 1
API Version: 0.2.9
movej motion succeeded
movej_p motion succeeded
Set force control mode succeeded
movel motion succeeded
movel motion succeeded
Stop force control mode succeeded
Set force control mode succeeded
movel motion succeeded
movel motion succeeded
Stop force control mode succeeded
Set force control mode succeeded
movel motion succeeded
movel motion succeeded
Stop force control mode succeeded
Successfully disconnected from the robot arm(2) After running the script, the trajectory from top to bottom is shown in the following image:
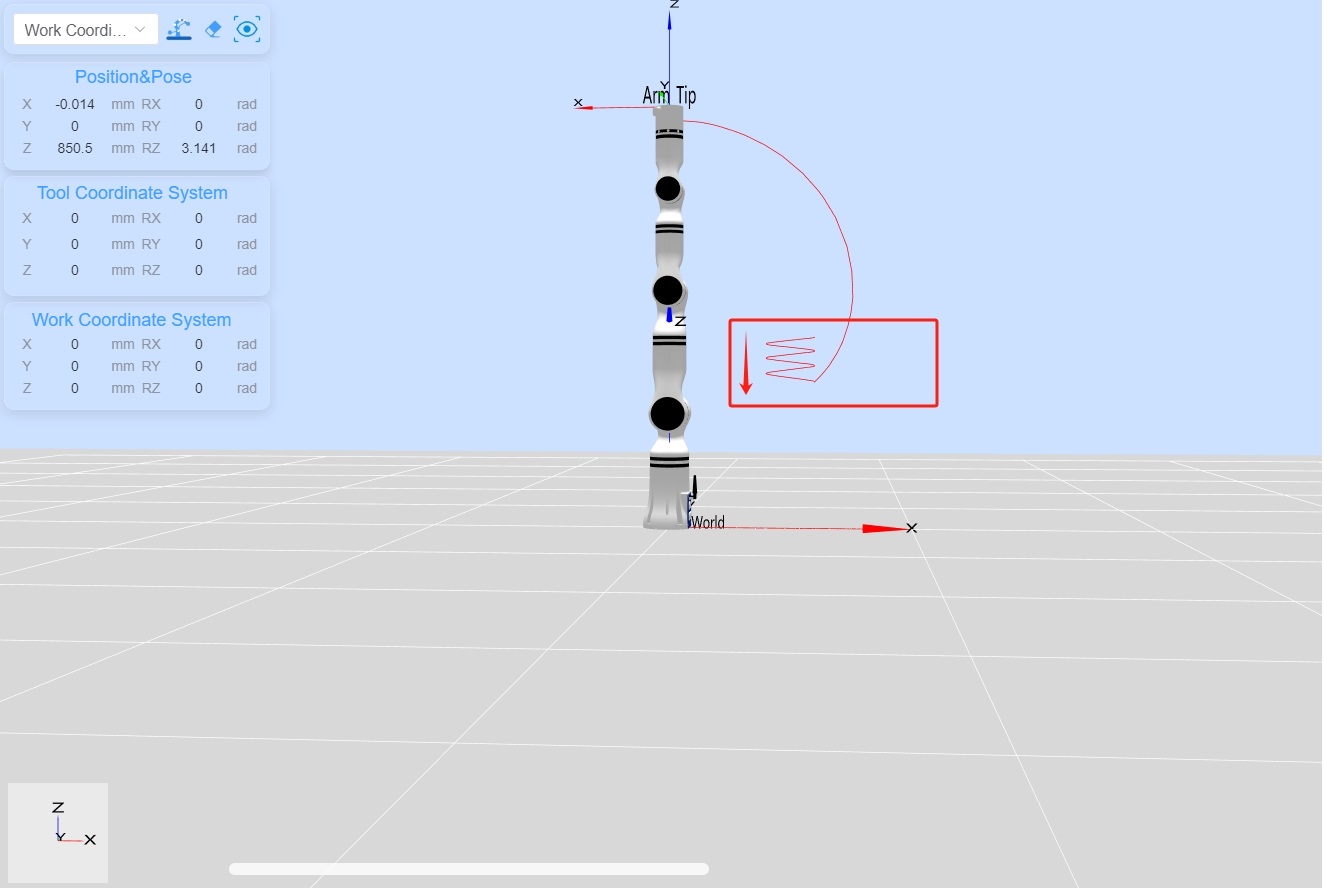
6.2 Code description
The following are the main functions of the demo_force_control.py file:
Connect the robotic arm
pythonrobot_controller = RobotArmController("192.168.1.18", 8080, 3)Connect the robotic arm to the specified IP address and port.
Get the API version
pythonprint("\nAPI Version: ", rm_api_version(), "\n")Get and display the API version.
Execute the movej motion
pythonrobot_controller.movej([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])Execute the movej_p motion
pythonrobot_controller.movej_p([0.3, 0, 0.4, 3.141, 0, 0])Enable the force control mode
pythonrobot_controller.set_force_position(sensor=1, mode=0, direction=2, force=-5)Execute the movel motion
pythonrobot_controller.movel([0.2, 0, 0.4, 3.141, 0, 0], v=50)Disable the force control mode
pythonrobot_controller.stop_force_position()Disconnect from the robotic arm
pythonrobot_controller.disconnect()
7. License information
- This project is subject to the MIT license.

